September 13, 2019
5g, LPWA, Innovation

Related Blogs:
Sign up for blog updates
Get innovation delivered to your inbox. Sign up for our blog and stay on top of the very latest from Semtech (formerly Sierra Wireless).
September 13, 2019
5g, LPWA, Innovation

Like many other foundational elements of the tech landscape, 5G – the 5th generation of cellular technology – isn’t arriving in a “big bang” but as a series of waves. As with 3G and 4G before it, 5G is following a path to commercialization that reflects what’s easiest to deploy.
A closer look reveals five distinct waves of 5G deployment – some of which are already underway, some of which are coming soon, and some of which are still a few years away. And, as we describe in our white paper, 5G for IoT? You’re Just in Time and webinar, 5G for IoT: Beyond the Hype, while some of these waves will be evolutionary in nature and involve incremental changes, other waves will be revolutionary, enabling exciting new use cases.
The first wave kicked off in earnest in 2019 and is focused on fixed wireless access deployments that deliver high speed cellular connectivity to a fixed location, such as a private home or business. With 5G fixed wireless services, homes and businesses will be able to get wireless broadband service that is as fast (or even faster) than many current wired broadband services.
Why is fixed wireless the first wave of 5G? Because it’s relatively quick and easy to roll out in small areas, and the business case is clear.
The second wave of 5G is focused on consumer cellular, primarily for smartphones. Chances are you are already seeing this wave emerge, as 2019 is widely viewed as the year that 5G smartphones, and the networks that support them, will really begin to take off. In fact, network operators are moving ahead with deployments, and smartphone manufacturers are introducing new models that are 5G-ready.
Wave 2 will address many Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB) use cases, with new high-bandwidth smartphone applications. Such use cases range from smartphone “Hot Spots” that are as fast as a Wi-Fi or other high-bandwidth connections, to very high quality “3G” video calls, to smartphone-based virtual reality (VR) or augmented reality (AR) applications.

In 2020, we will see eMBB extend beyond smartphones to other devices, with new use cases that benefit from 5G’s high peak and average speeds, spectrum efficiency and high capacity.
People will experience these new eMBB 5G applications in their cars, with new and enhanced navigation, infotainment, in-car Wi-Fi, predictive maintenance, insurance, EV-charging, and other connected car services. They will also experience them on their tablets, gaming devices and VR headsets, with mobile high-definition video streaming, 3D multi-player games and immersive AR and VR experiences.
With 5G, any barriers that prevented mobile cellular devices from delivering the same level of functionality or performance as devices with wired connections will be eliminated. This breakthrough will create opportunities not just for the use cases above, but others we have yet to even imagine.
In 2021, we will begin to see the rise of Wave 4, which will encompass the use of 5G to extend existing Low Power Wide Area(LPWA) Internet of Things (IoT) applications. These applications – and the IoT edge devices they depend on – have a wide range of requirements and use cases that 5G will address in different ways.
This fourth wave will primarily support Massive, Machine-Type Communication (mMTC) IoT use cases using (LPWA) technologies, which are designed for IoT applications that require low-cost devices, low-power usage, and a large number of connected edge devices in a given area. Examples of these types of mMTC use cases include large-scale deployments of LPWA devices (like sensors) for smart city, smart logistics, smart meter, and similar applications.
Since a software update is all that is required to take advantage of many of 5G’s enhanced capabilities for these mMTC use cases, enterprises can smoothly transition their applications from 4G to 5G when the time comes. Given this, rather than wait, enterprises should move ahead with any mMTC-type IoT application initiatives they are currently pursuing or planning – knowing that when 5G’s enhancements to LPWA become available, they will be able to quickly update their application to benefit from these enhancements.
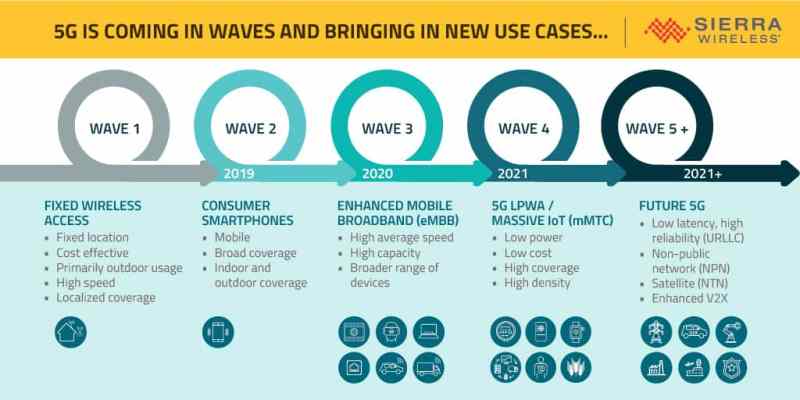
Wave 5+ centers around future use cases for 5G, and this wave isn’t expected until late 2021 or early 2022. The first four waves of 5G are really evolutions of existing cellular use cases, with important enhancements to fixed wireless access, high-speed, high-bandwidth mobile broadband, and LPWA mMTC applications. The 5+ wave represents a bigger leap forward, thanks to the capabilities enabled by 5G’s use of mmWave spectrum and other advancements that are part of the 5G New Radio (NR) standard.
5G NR will use mmWave, which is a different part of the wireless spectrum (between 20 GHz and 300 GHz) than existing cellular wireless networks. This different spectrum – along with 5G NR’s other technological advancements, such as a new core network – will deliver new groundbreaking capabilities that were impossible for cellular technologies to offer before, including ultra-high reliability, very low latency, and extremely fast handoffs.
With these new capabilities, companies will be able to develop applications for new Ultra-Reliable, Low-Latency Communications (URLLC) use cases. Think here of revolutionary new applications for the Industrial IoT (IIoT) or Industry 4.0, such as factory automation (aka smart factories), self-healing smart grids, and possibly even autonomous vehicles. In addition, 5G’s ability to deliver very low latency, very high reliability and very fast handoffs will likely result in new use cases emerging that haven’t even been conceived of yet.
Given the phased rollout of 5G’s new capabilities, there are a variety of ways for enterprises to “catch the 5G wave.” Most importantly, companies should not “panic” and hold off on their current IoT initiatives, waiting for 5G – especially since 5G has been designed to coexist with 4G, extending 4G’s lifespan.
For example, companies can continue their current LPWA initiatives, knowing that they can take advantage of 5G’s enhanced mMTC capabilities when they become available in Wave 4. In addition, now is the perfect time for enterprises to start thinking how they might be able to transform their businesses using the groundbreaking new ultra-high reliability, very low latency, and other URLLC capabilities that will be available in 5G Wave 5+.
In both cases, enterprises should ask themselves: what type of 5G use cases might enable them to reimagine their future? Whatever use cases do make sense for them, Sierra Wireless can provide the 5G knowledge, solutions, and expertise needed to realize their IoT goals. Read our white paper, 5G for IoT? You’re Just in Time, watch our webinar, 5G for IoT: Beyond the Hype, and Start with Sierra to learn more on how your organization can use 5G to thrive in the connected economy.
Get innovation delivered to your inbox. Sign up for our blog and stay on top of the very latest from Semtech (formerly Sierra Wireless).